Classification, Properties, and Management of Aridisols
Suborders and Great Groups
 |
In addition to diagnostic horizons and soil moisture regimes, ten
soil temperature regimes are very important for classification of
soils in Soil Taxonomy. For example, one of the seven suborders
of the Aridisol Order is differentiated by the upper boundary of
the cryic soil temperature regime, 0º to 8º C. Cryids
are Aridisols with soil temperatures between 5º and 8º
C, 5º is the lower temperature limit of Aridisols, 8º
is the upper limit of cryic soil temperature regime. The Suborders
of Aridisols have undergone major changes since the 1975 edition
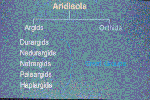
of Soil Taxonomy. Originally there were only two Suborders, Argid
which still remains and Orthid which has been deleted, its soils
placed into new classes. Argids are differentiated by the presence
or absense of horizons having silicate clay enrichment. Argids
have argillic or natric horizons. Orthid was a catch-all
class that lacked horizons of clay enrichment. For the reclassification
of Suborders, many of the diagnostic horizons that were used to
differentiate Argids and Orthids at the next lower taxonomic level
(Great Group) were elevated to Suborder criteria.
|
 |
The next level of Soil Taxonomy is the Great Group.
Great groups represent subdivisions of suborders based on similar
kind, arrangement, and degree of expression of horizons. For example,
the six Argid Great Groups are differentiated by the amount of clay
in the argillic horizon and by the type of associated subsurface
diagnostic horizons. Argid Great Groups have also been modified
since the 1975 edition of Soil Taxonomy. Two Great Groups have been
deleted, Durargids and Nadurargids. Three Great Groups have been
added, Petroargids, Gypsiargids, and Calciargids.
|
Introduction to Aridic Soils | Soil Taxonomy | Introduction to
Soil Horizons | The Horizons | Suborders
and Great Groups | Argid Suborder | Orthid
Suborder | Subgroups | Families
| Non-Aridisols | Irrigation
| Saline Soils | Sodic
and Saline-Sodic Soils | Final Considerations
|