--June 3, 2002 Version--
I. Definitions
Definition #1. Putative Resistance Event--A Cautionary Alert
A putative resistance event consists of any field of Bt cotton in which collections of 100 bolls yield 3% or more large larvae (3rd instar or later), pupae or PBW exit holes in bolls and a test indicates that bolls from which large larvae were recovered were expressing Bt. This is a cautionary alert and must not be construed to be a verified resistance event until: 1) the plants from which collections were made are confirmed to produce Bt toxin and, 2) bioassays are completed that confirm the reduced susceptibility of the pink bollworm surviving on Bt cotton.
Definition #2. A Verified Resistance Event.
A putative resistance event becomes verified if three conditions are met:
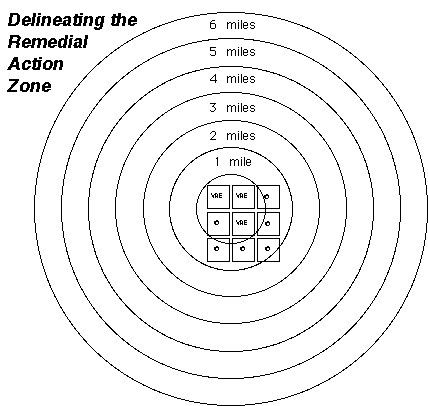
II. Remedial Action
A. Putative Resistance Event: Year of First Detection.
Once a putative resistance event occurs, alternative PBW controls should be implemented in that field. Measures should include one or more of the following:

III. Recommended Organizational Roles
IV. Select Resistance References from the AZ Bt Cotton Working Group
Bartlett, A.C., T.J. Dennehy and Larry Antilla. 1997. An evaluation of resistance to B.t. toxins in native populations of the pink bollworm. Proc. 1997 Beltwide Cotton Conferences. pp. 918-921.
Simmons, A. L., T. J. Dennehy, B. E. Tabashnik, L. Antilla, A. Bartlett, D. Gouge, and R. Staten. 1998. Evaluation of B.t. cotton deployment strategies and efficacy against pink bollworm in Arizona. Proc. 1998 Beltwide Cotton Conf. 2: 1025-1030.
Liu, Y. B., B. E. Tabashnik, T. J. Dennehy, A. L. Patin, A. C. Bartlett. 1999. Development time and resistance to Bt crops. Nature 400: 519.
Patin, A. L., T. J. Dennehy, M. A. Sims, B. E. Tabashnik, Y. B. Liu, L. Antilla, D. Gouge, T. J. Henneberry and R. Staten. 1999. Status of pink bollworm susceptibility to B.t. in Arizona. Proc. 1999 Beltwide Cotton Conf. 2: 991-996.
Tabashnik, B. E., A. L. Patin, T. J. Dennehy, Y. B. Liu, E. Miller and R. Staten. 1999. Dispersal of pink bollworm (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) males in transgenic cotton that produces a Bacillus thuringiensis toxin. J. Econ. Entomol. 92: 772-780.
Walters, M., R. Staten, R. Sequeira, and T.J. Dennehy. 1999. Preliminary analysis of pink bollworm population distributions in a large acreage of genetically engineered cotton with regard to resistance management. Proc. 1999 Beltwide Cotton Conferences. pp.989-991.
Tabashnik, B. E., Y. B. Liu, R. A. deMaagd and T. J. Dennehy. 2000. Cross-resistance of pink bollworm (Pectinophora gossypiella) to Bacillus thuringiensis toxins. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66: 4582-4584.
Tabashnik, B. E., A. L. Patin, T. J. Dennehy, Y. B. Liu, Y. Carrière, M. A. Sims, and L. Antilla. 2000. Frequency of resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis in field populations of pink bollworm. Proc. Nat'l. Acad. Sci. USA 97: 12,980-12,984.
Tabashnik, B. E., R. T. Roush, E. D. Earle, A. M. Shelton. 2000. Resistance to Bt toxins. Science 287: 42.
Antilla, L., M. Whitlow, B. Tabashnik, T. Dennehy and Y. Carrière. 2001. Benefits of multi-level monitoring activities for a pink bollworm resistance management program in transgenic (Bt) cotton in Arizona. 2001 Proc. Beltwide Cotton Conf. 2: 1173-1175.
Carrière, Y., C. Ellers-Kirk, B. Pederson, S. Haller, and L. Antilla. 2001. Predicting spring moth emergence in the pink bollworm: implications for managing resistance to transgenic cotton. J. Econ. Entomol. 94: 1012-1021.
Carrière, Y., T. J. Dennehy, B. Pedersen, S. Haller, C. Ellers-Kirk, L. Antilla, S. Haller, Y. B. Liu, E. Willott and B. E. Tabashnik. 2001. Large-scale management of insect resistance to transgenic cotton in Arizona: can transgenic insecticidal crops be sustained? J. Econ. Entomol. 94: 315-325.
Carrière, Y., C. Ellers-Kirk, Y. B. Liu, M. A. Sims, A. L. Patin, S. Meyer, T. J. Dennehy and B. E. Tabashnik. 2001. Fitness costs and maternal effects associated with resistance to transgenic cotton in the pink bollworm (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 94: 1571-1576.
Carrière, Y., C. Ellers-Kirk, A. L. Patin, M. Sims, S. Meyer, Y. B. Liu, T. J. Dennehy and B. E. Tabashnik. 2001. Overwintering cost associated with resistance to transgenic cotton in the pink bollworm. J. Econ. Entomol. 94: 935-941.
Carrière, Y., and B. E. Tabashnik. 2001. Reversing insect adaptation to transgenic insecticidal plants. Proc. Roy. Soc. London B 268: 1475-1480.
Herrero, S., J. González-Cabrera, B. E. Tabashnik and J. Ferré. 2001. Shared binding sites in Lepidoptera for Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ja and Cry1A toxins. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67: 5729-5734.
Liu, Y. B., B. E. Tabashnik, S. K. Meyer, Y. Carrière and A. C. Bartlett. 2001. Genetics of pink bollworm resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis toxin Cry1Ac. J. Econ. Entomol. 94: 248-252.
Liu, Y. B., B. E. Tabashnik, S. K. Meyer, and N. Crickmore. 2001. Cross-resistance and stability of resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis toxin Cry1C in diamondback moth. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67: 3216-3219.
Liu, Y. B., B. E. Tabashnik, T. J. Dennehy, Y. Carrière , M. A. Sims and S. K. Meyer, and Y. Carrière. 2001. Effects of Bt cotton and Cry1Ac toxin on survival and development of pink bollworm (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 94: 1237-1242.
Meyer, S. K., B. E. Tabashnik, Y. B. Liu, M. C. Wirth and B. A. Federici. 2001. Cyt1A from Bacillus thuringiensis lacks toxicity to susceptible and resistant larvae of diamondback moth and pink bollworm. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67: 462-463.
Moulton, J.K. and T.J. Dennehy. 2001. Beet armyworm resistance to Cry1Ac. Proceedings Beltwide Cotton Conferences. National Cotton Council. pp. 989-991.
Sims, M. A., T. J. Dennehy, A. Patin, Y. Carrière, Y. B. Liu, B. E. Tabashnik, L. Antilla, and M. Whitlow. 2001. Arizona’s multi-agency resistance management program for Bt cotton: sustaining the susceptibility of pink bollworm. 2001 Proc. Beltwide Cotton Conf. 2: 1175-1179.
Tabashnik, B. E. 2001. Breaking the code of resistance. Nature Biotechnology 19: 922-924.
Tabashnik, B. E., T. J. Dennehy and Y. Carrière. 2001. Supporting a cautious approach to agricultural biotechnology. BioScience 51: 905-906.
Liu, Y. B., B. E. Tabashnik, T. J. Dennehy, Y. Carrière, M. A. Sims and S. K. Meyer. 2002. Oviposition on and mining in bolls of Bt and non-Bt cotton by resistant and susceptible pink bollworm (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 95: 143-148.
Sims, M. A., T. J. Dennehy, L. Shriver, D. Holley,Y. Carrière and B. E. Tabashnik. 2002. Susceptibility of Arizona pink bollworm to Cry1Ac. 2002. Proc. Beltwide Cotton Conf. National Cotton Council, Memphis, TN.
Tabashnik, B. E. T. J. Dennehy, Y. Carrière, Y. B. Liu, S. K. Meyer, A. Patin and M. A. Sims. 2002. Resistance management: slowing pest adaptation to transgenic crops. Acta Scandinavica, Section B, Soil and Plant Science: in press.
Tabashnik, B. E., Y. B. Liu, T. J. Dennehy, M. A. Sims, M. S. Sisterson, R. W. Biggs and Y. Carrière. 2002. Inheritance of resistance to Bt toxin Cry1Ac in a field-derived strain of pink bollworm (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae). J. Econ. Entomol.: in press.
Tabashnik, B. E. 2002. Review of "Lords of the Harvest: Biotech, Big Money, and the Future of Food" by Daniel Charles. Quarterly Review of Biology. In press.
Tabashnik, B. E. 2002. Pesticide resistance. Pp. 880-883, In: M. Pagel (ed.), Encyclopedia of Evolution.