 Well Owner Education - August 1, 2018 Jeff Schalau, Agent, Agriculture & Natural Resources University of Arizona Cooperative Extension, Yavapai County Many Yavapai County households are dependent on private wells for their domestic water supply. There is much to know about well placement, maintenance, water quality testing, and interpreting well test results. The University of Arizona Cooperative Extension has developed several publications and educational programs to help Arizona citizens understand and maintain their wells. All wells in Arizona are regulated by Arizona Department of Water Resources (ADWR). Before anyone can drill a new well or deepen or modify an existing well, that person must obtain authorization from ADWR. The well must meet minimum construction standards and must be drilled by a licensed well drilling contractor. In the Prescott area, well pumping rules are more stringent because the area has been designated by the ADWR as an Active Management Area (AMA). Outside the AMA (which includes all of the Verde Valley), there are no pumping restrictions or reporting rules. However, all new wells must be permitted through the Yavapai County Development Services, in cooperation with the ADWR. The substrate into which the well is drilled will determine the quantity and quality of water produced by the well. This substrate is called an aquifer. Many well owners erroneously think their well taps into an underground lake or cave, but this is rarely the case. The aquifer is an underground geologic formation capable of transmitting and yielding usable quantities of water to a well or spring. Depending on the geologic formation, water is typically held in subsurface fractures and cracks of rock, or in interconnected pores and void spaces between grains of sand and gravel or soil. The water extracted by the well is called “ground water”. Ground water in contact with naturally occurring minerals of the rocks and alluvium will dissolve and transport those minerals to your well and water supply. In Yavapai County, the most common naturally occurring water supply contaminants are arsenic and radon. Human activities can also influence well water quality. Nitrate contamination is most often caused by human activity on the land, and has been linked to irrigated agriculture, concentrated livestock facilities, large turf areas, and septic systems. Other human-introduced contaminants that can enter the aquifer include chemicals, pesticides, used oil, fuel, cleaners, and pharmaceuticals. These can enter the aquifer through septic systems or by spills occurring at the soil surface or near the wellhead. Well water quality is not regulated and it is the homeowner’s responsibility to ensure the safety of their well’s drinking water. Cooperative Extension and the National Ground Water Association recommend well owners test their well water annually for bacteria and nitrates. Depending on the geology of the aquifer, it may be wise to also test annually for arsenic and radon (both are naturally occurring ground water contaminants). Information on these areas and water treatment alternatives are included in the various resources linked to the online edition of this column (see URL below). ADWR also maintains records of existing wells. Much of this information is available through the online application called Well Registry - ADWR GIS (also linked to the online edition). Here, you may query the well records to identify the well location, well owner, well depth, depth to ground water, well construction materials, well driller/maintenance dates, and other related information. Some of these wells also have historic monitoring data indicating changes in depth to groundwater. As stated above, it is the responsibility of the private well owner to manage the well and ensure its water is safe to drink. Public Water Systems (those having at least fifteen service connections, or regularly services at least twenty-five persons for at least sixty days a year) are regulated by the Arizona Department of Environmental Quality (ADEQ). Municipal water systems are regulated by the city or town council and must also adhere to ADEQ guidelines. Would you like to learn more about private well operation and maintenance? The University of Arizona Cooperative Extension is offering a Well Owner Workshop on August 18, 2018 between 1 and 3:30 pm at the Cottonwood Recreation Center. The workshop is free. Reservations can be made by calling or e-mailing Lydia Watts at 928-445-6590 ext. 221 or lydiawatts@email.arizona.edu. Space is limited and I hope to see you there! Follow the Backyard Gardener on Twitter – use the link on the BYG website. If you have other gardening questions, call the Master Gardener help line in the Camp Verde office at 928-554-8992 or e-mail us at verdevalleymg@gmail.com and be sure to include your name, address and phone number. Find past Backyard Gardener columns or provide feedback at the Backyard Gardener web site: http://cals.arizona.edu/yavapai/anr/hort/byg/. 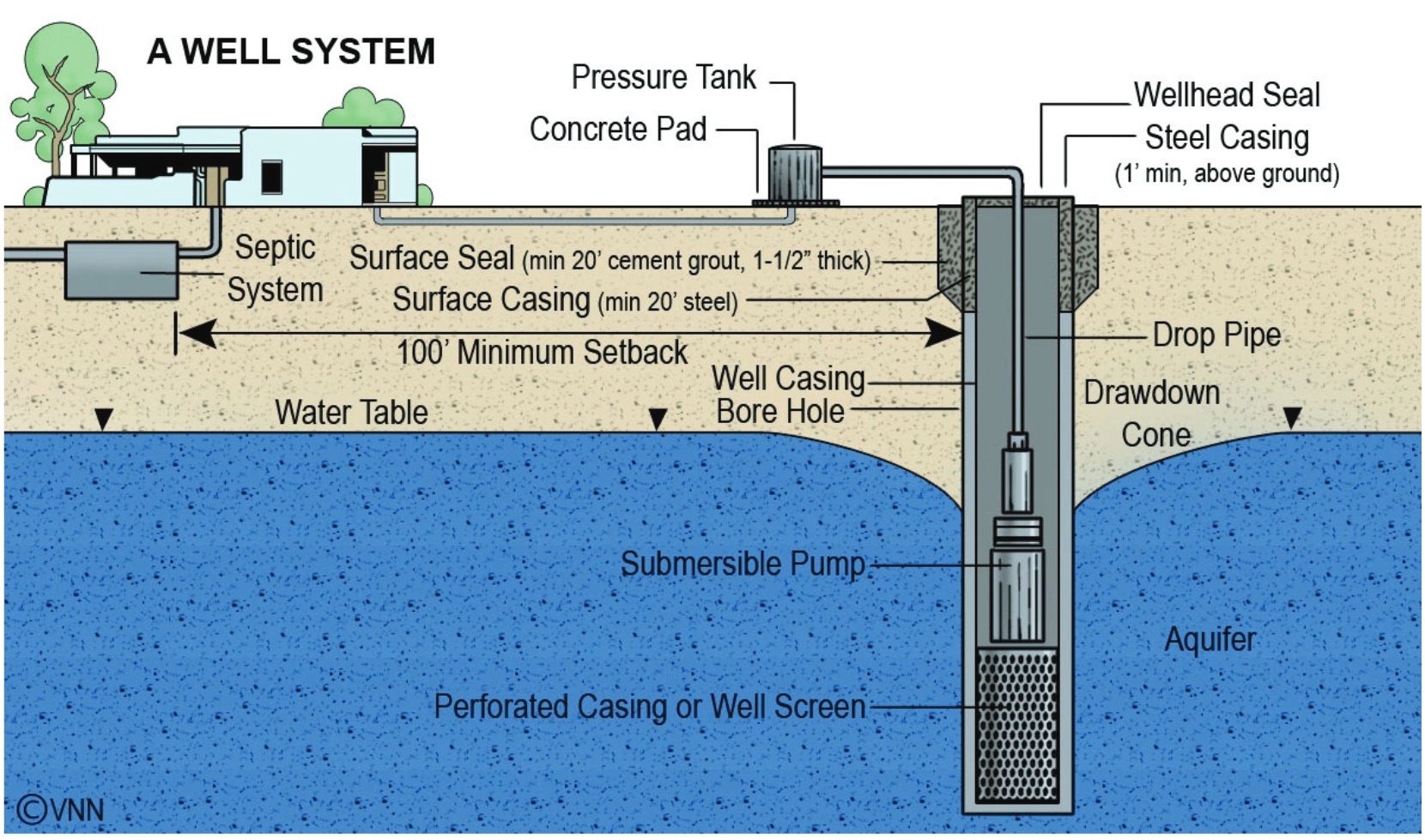 Schematic of a well including wellhead, casing, submersible pump, and other components (from: ADWR Well Owners Guide).
Schematic of a well including wellhead, casing, submersible pump, and other components (from: ADWR Well Owners Guide).Well Owner Resources Arizona Well Owners Video Series University of Arizona Cooperative Extension extension.arizona.edu/pubs/arizona-well-owners-video-series Arizona Well Owner's Guide To Water Supply, 2nd Edition University of Arizona Cooperative Extension extension.arizona.edu/sites/extension.arizona.edu/files/pubs/az1485-2017_0.pdf Private Water Well Components University of Arizona Cooperative Extension extension.arizona.edu/sites/extension.arizona.edu/files/pubs/az1486b.pdf Arizona Domestic Water Wells University of Arizona Cooperative Extension extension.arizona.edu/sites/extension.arizona.edu/files/pubs/az1504-2015.pdf Private Well Protection University of Arizona Cooperative Extension extension.arizona.edu/sites/extension.arizona.edu/files/pubs/az1486e.pdf Maintaining Private Water Well Systems University of Arizona Cooperative Extension extension.arizona.edu/sites/extension.arizona.edu/files/pubs/az1486d.pdf Arizona Wells: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Wells University of Arizona Cooperative Extension extension.arizona.edu/sites/extension.arizona.edu/files/pubs/az1581.pdf Arizona Wells: Low Yielding Domestic Water Wells University of Arizona Cooperative Extension extension.arizona.edu/sites/extension.arizona.edu/files/pubs/az1537.pdf Well Water Testing and Understanding the Results University of Arizona Cooperative Extension extension.arizona.edu/sites/extension.arizona.edu/files/pubs/az1486f.pdf An Arizona Guide to Domestic Well Registration and Record-Keeping University of Arizona Cooperative Extension extension.arizona.edu/sites/extension.arizona.edu/files/pubs/az1663-2015.pdf An Arizona Guide to Domestic Well Registration and Record-Keeping University of Arizona Cooperative Extension extension.arizona.edu/sites/extension.arizona.edu/files/pubs/az1663-2015.pdf Well Owners' Guide to Ground Water Resources in Yavapai County University of Arizona Cooperative Extension extension.arizona.edu/sites/extension.arizona.edu/files/pubs/az1451.pdf Arizona Drinking Water Well Contaminants University of Arizona Cooperative Extension extension.arizona.edu/sites/extension.arizona.edu/files/pubs/az1503.pdf Microorganisms in Private Water Wells University of Arizona Cooperative Extension extension.arizona.edu/sites/extension.arizona.edu/files/pubs/az1486h.pdf Obtaining a Water Sample for Bacterial Analysis University of Arizona Cooperative Extension extension.arizona.edu/sites/extension.arizona.edu/files/pubs/az1486g.pdf What Well Owners Should Know about Shock Chlorination University of Arizona Cooperative Extension extension.arizona.edu/sites/extension.arizona.edu/files/pubs/az1605.pdf Nitrate in Private Water Wells University of Arizona Cooperative Extension extension.arizona.edu/sites/extension.arizona.edu/files/pubs/az1486i.pdf Nitrate Contamination Potential in Arizona Groundwater: Implications for Drinking Water Wells University of Arizona Cooperative Extension extension.arizona.edu/sites/extension.arizona.edu/files/pubs/az1536.pdf Arsenic in Private Water Wells University of Arizona Cooperative Extension extension.arizona.edu/sites/extension.arizona.edu/files/pubs/az1486k.pdf Arsenic in Arizona Ground Water -- Source and Transport Characteristics University of Arizona Cooperative Extension extension.arizona.edu/sites/extension.arizona.edu/files/pubs/az1453.pdf How to Lower the Levels of Arsenic in Well Water: What Choices do Arizona Consumers Have? University of Arizona Cooperative Extension extension.arizona.edu/sites/extension.arizona.edu/files/pubs/az1650-2015.pdf Matching Drinking Water Quality Problems to Treatment Methods University of Arizona Cooperative Extension extension.arizona.edu/sites/extension.arizona.edu/files/pubs/az1486l.pdf Well Registry Web Arizona Department of Water Resources An online application to find well registry numbers, owner information, associated water rights, & pumping data. gisweb.azwater.gov/waterresourcedata/wellregistry.aspx |