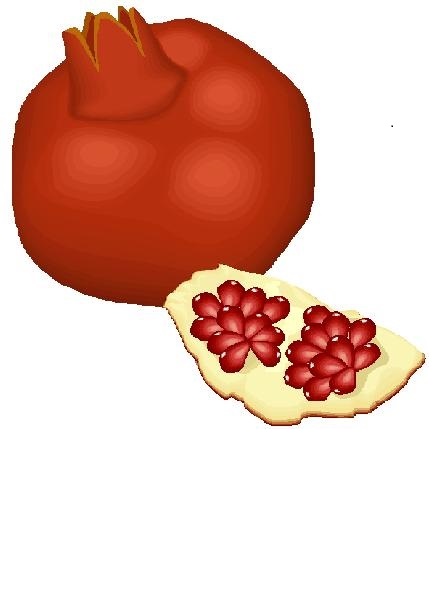
 Pomegranates - November 12, 2008 Jeff Schalau, Associate Agent, Agriculture & Natural Resources University of Arizona Cooperative Extension, Yavapai County Pomegranates (Punica granatum) are native to southeastern Europe and Asia and have been cultivated in ancient Egypt, Babylonia, India, and Iran. The Spanish brought them to Mexico, California, and Arizona in the 16th century. Although pomegranates have not attained the popularity of other fruits, they are worthy of a place in your backyard garden. Pomegranates are easy to grow, have beautiful flowers, are well suited to our desert environment, and have the added benefit of producing delicious fruit. The fruit has flesh-covered seeds can be used as a garnish in fruit cups, salads, desserts, and as a snack. The juice is used in making jellies, puddings, desserts, wine and fruit drinks. Grenadine, made from pomegranate juice, is indispensable in flavoring some beverages. More recently, pomegranates have become increasingly popular for their healthful antioxidant qualities. Pomegranates grow on woody plants that more closely resemble shrubs than trees. Mature plants are usually 6 to 12 feet in height and can be trained to a tree form. Pomegranate plants are deciduous, have small oval leaves, and are somewhat thorny. They require full sun, tolerate alkaline soils, summer heat, and winter lows to 10 degrees F. They are somewhat drought tolerant, but should be irrigated similar to other fruit trees for optimum fruit quality. Mature fruits are 2 to 5 inches in diameter, have purple to reddish skin (some varieties are pink), which contain hundreds of seeds. The fruits resemble apples but are actually berries and ripen between September and December. Inside the tough outer skin are seeds, each surrounded by a membrane that encloses a juicy pulp: this is the edible portion of the fruit. The juice is somewhat tart and the seed has a slight nutty flavor. Pomegranates are often juiced and are sometimes used to make jelly. Handle pomegranate fruit carefully as they bruise easily. Properly stored fruit will retain its freshness and flavor over an extended period of time. Harvested fruit should be stored in a cool area (40-50 degrees F). Ripening will continue to full flavor at these temperatures. Fruit stored at 32-40 degrees F will keep for weeks/months, especially at high relative humidity (80% or greater). Pomegranates are usually available from nurseries but you may need to call around to locate them. ‘Wonderful’ is a common fruiting variety suitable for the Verde Valley, but there are several other suitable varieties. There are also flowering varieties available but these produce small, inedible fruit. Pomegranates can be grown from seed, but should be propagated from cuttings to ensure consistent fruit quality and characteristics. As stated above, pomegranates often have a shrubby growth form. This is because they produce many suckers from the root and crown area. If a shrub-type plant is preferred, leave five or six main shoots. Each year, remove one of the old shoots and leave a new basal shoot to replace it. Plants trained to multiple trunks require less frequent care and pruning and come into bearing sooner than plants with only one trunk. To encourage a tree-like form, you can select one trunk and will need to remove suckers on a regular basis. Three to five scaffold branches should be selected starting about 10 inches above the soil level and spaced 4 to 6 inches apart along the trunk. Pomegranate trees are self-fruitful, so a second tree is unnecessary for pollination. Severe fruit drop during the plant's juvenile period (3-5 years) is not uncommon. Mature trees seem to set and hold fruit better than younger trees. Once established, a very light application of nitrogen fertilizer in the spring can enhance fruit quality and plant vigor. Pomegranates also have other uses. For instance, a red dye can be extracted from the flowers, a yellow dye from the skin of the fruit, and a black dye from the roots. The wood is also very hard, close-grained, and durable. The plant also contains several alkaloids and tannins in the bark and roots and has been used medicinally for more than 3,000 years. The University of Arizona Cooperative Extension has publications and information on gardening and pest control. If you have other gardening questions, call the Master Gardener line in the Cottonwood office at 646-9113 ext. 14 or E-mail us at cottonwoodmg@yahoo.com and be sure to include your address and phone number. Find past Backyard Gardener columns or submit column ideas at the Backyard Gardener web site: http://cals.arizona.edu/yavapai/anr/hort/byg/. |